Now that we understand the concept of Data Warehouse, its importance and usage, it’s time to gain insights into the custom architecture of DWH.
There are two main components to building a data warehouse- an interface design from operational systems and the individual data warehouse design. Thus, the construction of DWH depends on the business requirements, where one development stage depends on the results of previously developed phase. The structure of a DWH can be understood better through its layered model, which lists the main components of the data warehousing architecture.
Below is the typical architecture of data warehouse consisting of different important components.
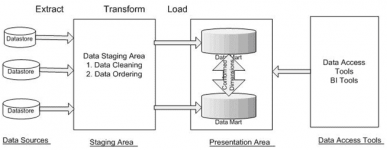
You can see that it is nothing but the movement of data from source to staging area and then finally to conformed data marts through ETL (Extract, Transform and Load) technology.
The first layer is the
Data Source layer, which refers to various data stores in multiple formats like relational database, Excel file and others. These stores can consists of different types of data – Operational data including business data like Sales, Customer, Finance, Product and others, web server logs, Internet research data and data relating to third party like census, survey.
The next step is
Extract, where the data from data sources is extracted and put into the warehouse staging area. The extracted data is minimally cleaned with no major transformations.
Then comes the
Staging area, which is divided into two stages – data cleaning and data ordering. As the name suggests, this layer takes care of data processing methods, i.e. cleaning (removing data redundancy, filtering bad data) and ordering (allowing proper integration) of data. Overall, this stage allows application of business intelligent logic to transform transactional data into analytical data. It is indeed the most time consuming phase in the whole DWH architecture and is the chief process between data source and presentation layer of DWH.
Major fuctions and services in the data storage area:
Basic Functions of a Warehouse
Basic function of a warehouse are movement of goods storage of goods, and information management.
1. Storage of Goods: One of the traditional requirements of a warehouse has been for storing goods. The warehouse provides the space required for such storage and it is one of the important functions of a warehouse.
Warehouse performs two types of storage: planned and extended.
Planned Storage:
Storage required as planned to meet the regular customer demand is called panned storage, Every inventory in received in the warehouse requires storage for a certain period of time. The duration of storage many vary.
Extended Storage:
Extended storage is an inventory in excess of normal warehouse operation. Some of the reasons for extended storage requirements are seasonality in demand, erratic demand, product conditioning, speculative purchases, discounts, etc.
To meet the erratic or seasonality in demand an additional storage of goods in terms of safety stocks could be required.
Some products such as food items may be stored for conditioning purposes. E.g. ripening of fruits.
Sometimes a firm may buy bulk quantities to avail of the discounts that are available or to purchase when the price is low. This is speculative purchases as the goods are bought at a higher quantity due to lower price or due to expectation of higher price in the future.
Sometimes due to promotional campaigns such as sales promotion, additional stock may be required to be kept to meet the expected higher demand for the product.
2. Movement of Goods: Movement of goods consist of inbound activity (unloading of goods brought to warehouse), transfer to storage (transferring the goods from the inbound area to the storage area), order selecting (selecting the good in the storage as per order to be shipped and transferring it to shipment area) and outbound activity (checking and loading the gods for shipment).
3. Information Management: Keeping a track of information regarding goods that have come into the warehouse, stored and that are shipped out of the warehouse. Also any other information pertaining to the warehouse is stored. The data captured by the information system in the warehouse is then passed on to the higher management in order to take better decisions.
Secondary Functions of a Warehouse
4. Protection of goods- A warehouse provides protection to goods from loss or damage due to heat, dust, wind and moisture, etc. It makes special arrangements for different products according to their nature. It cuts down losses due to spoilage and wastage during storage.
5. Risk bearing – Warehouses take over the risks incidental to storage of goods. Once goods are handed over to the warehouse-keeper for storage, the responsibility of, these goods passes on to the warehouse-keeper. Thus, the risk of loss or damage to goods in storage is borne by the warehouse keeper. Since it is bound to return the goods in good condition, the warehouse becomes responsible for any loss, theft or damage etc., thus, it takes all precautions to prevent any mishap.
6. Financing- When goods are deposited in any Warehouse, the depositor gets a receipt, which acts as a proof about the deposit of goods. The Warehouses can also issue a document in favour of the owner of the goods, which is called warehouse-keeper’s warrant. This warrant is a document of title and can be transferred by simple endorsement and delivery. So while the goods are in custody of the warehouse-keeper, the businessmen can obtain loans from banks and other financial institutions keeping this warrant as security. In some cases, warehouses also give advances of money to the depositors for a short period keeping their goods as security.
7. Processing – Certain Commodities are not consumed in the form they are produced. Processing is required to make them consumable. For example, paddy is polished, timber is seasoned, and fruits are ripened, etc. Sometimes warehouses also undertake these activities on behalf of the owners.
8. Grading and branding- On request warehouses also perform the functions of grading and branding of goods on behalf of the manufacturer, wholesaler or the importer of goods. It also provides facilities for mixing, blending and packaging of goods for the convenience of handling and sale
1)Data warehouse architecture is just an overall guideline. It is not a blueprint for the
data warehouse
ans: False
2)In a data warehouse, the metadata component is unique, with no truly matching
component in operational systems
ans:True
2)You have been recently promoted to administrator for the data warehouse of a nationwide
automobile insurance company. You are asked to prepare a checklist for selecting a
proper vendor tool to help you with the data warehouse administration. Make a list of
the functions in the management and control component of your data warehouse archi-
tecture. Use this list to derive the tool-selection checklist.
Ans) Checklist: Can your tool satisfy the following?
Data Acquisition Functions:
Data Extraction
Select data sources
Determine filters for individual sources
Create system automated extract files from operation systems
Create intermediary files to store selected data to be merged later
Transport extracted files from multiple platforms
Provide automated job control services for creating extract files
Reformat input from outside sources, departmental data files, databases, and spreadsheets.
Create common application codes for data extraction Data Transformation: Map input data to data in DW repository
Clean data, deduplicate, and merge/purge
Denormalize extracted data structures as required by the dimensional model of the DW
Convert data types
Calculate and derive attribute values
Check for referential integrity
Aggregate data as needed
Resolve missing values
Consolidate and integrate data Data Staging
Provide backup and recovery for staging area repositories
Sort and merge files
Create files as input to make changes to dimension tables
Preserve audit trail to relate each data item int eh DW to input source
Consolidate datasets and create flat files for loading through DBMS utilities
3) As the senior analyst responsible for data staging, you are responsible for the design of the
data staging area. If your data warehouse gets input from several legacy systems on mul-
tiple platforms, and also regular feeds from two external sources, how will you organize
your data staging area? Describe the data repositories you will have for data staging.
Ans)


You can find it in PDF version :



